Nationwide Inventory of Intangible Cultural Heritage
Regional Diversity of Dialect Theatre in Germany
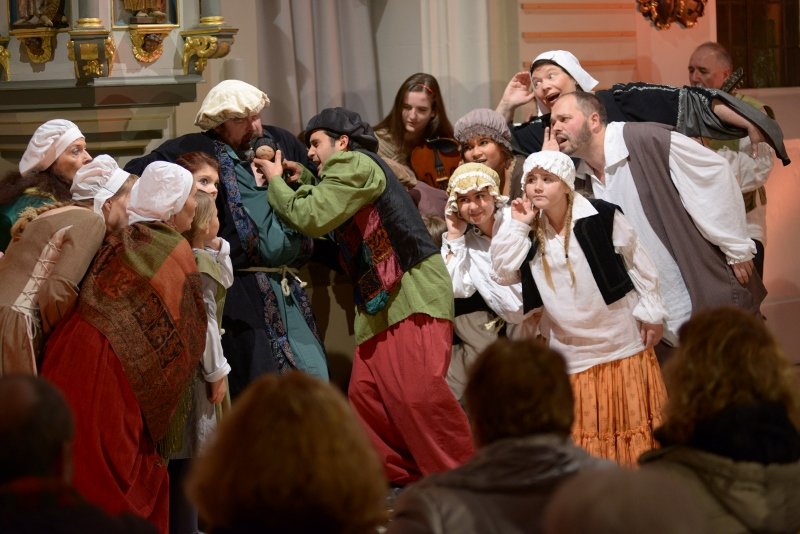
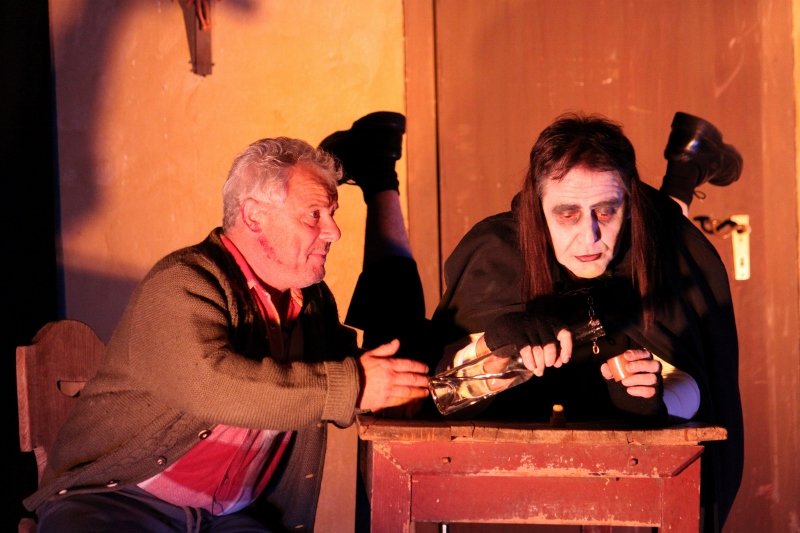
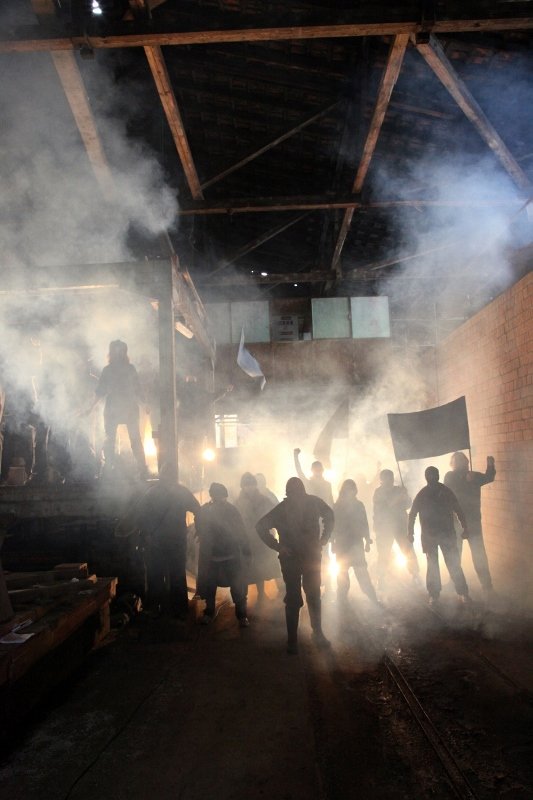
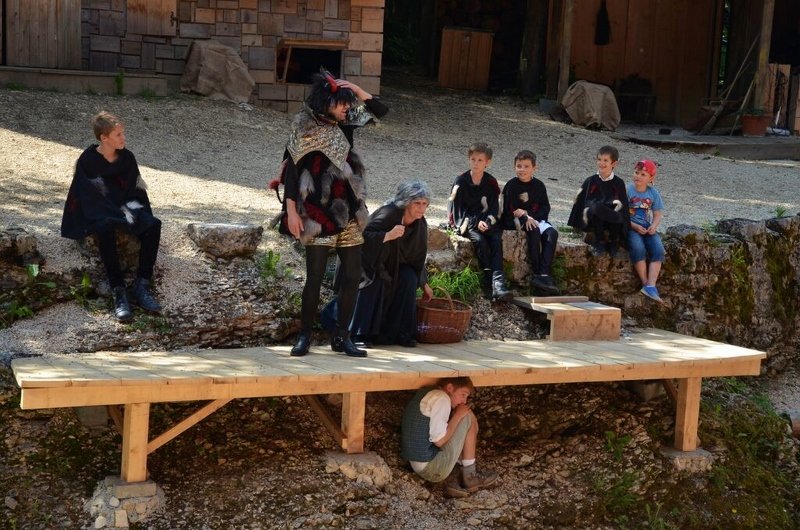
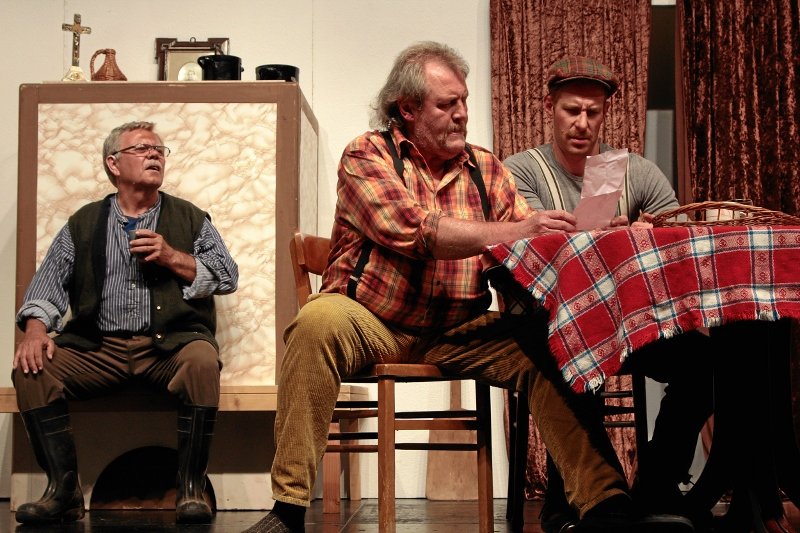
Dialect theater and oral folk theater is practiced by several thousand amateur stages, more than a thousand of which are organized in associations. This includes children's and youth theater departments. The repertoire of the folk theaters ranges from passion plays across idealizing, popular farces, drolleries and rural Heimat plays to critical analyses of humans’ history and everyday life.
Facts & figures
Crucial date: all seasons
Inscription: 2016
Domains: oral traditions and expressions; performing arts
Where to find: nationwide
Contact
Bund Deutscher Amateurtheater e.V.
@email
www.bdat.info
In general, the genre of comedy dominates. Myths, sagas and legends as well as ideas of how life could have been serve as material. Performances are held in inns, historical theaters and on open-air stages.
Qualities of the dialect theater strengthen the culture in rural areas. It is in dialogue with the local population and with local history and present. The dialect theater is committed to regional identity, the cultivation of tradition and dialects. Despite regional and local differences, there are similarities with regard to the genesis of materials, topic-finding, actors or stylistic formation of the content.
Dialect theater has a social, recreational function. Its cultural and social value develops within the triangle of dialect, theater play and honorary office: Honorary office as a citizen's commitment, dialect as an oral tradition, and theater as a direct artistic form of expression evoke identity and Heimat with all participants.
Dialect theater has emerged as an alternative to high culture and reflects bourgeois society since the 19th century. The cultural practice is passed on from generation to generation in dialect theaters, e.g. in the “Ritterschauspielen Kiefersfelden” since 1750. Playing theater in the "own" dialect allows the actor an individual authentic expression. It unfolds an integrative force. "Kiezdeutsch" also has long since become the dialect of migration. In the immigration society, the dialect theater forms an integrative form of participation and contributes to the acquisition of language and the dialogue between cultures.







